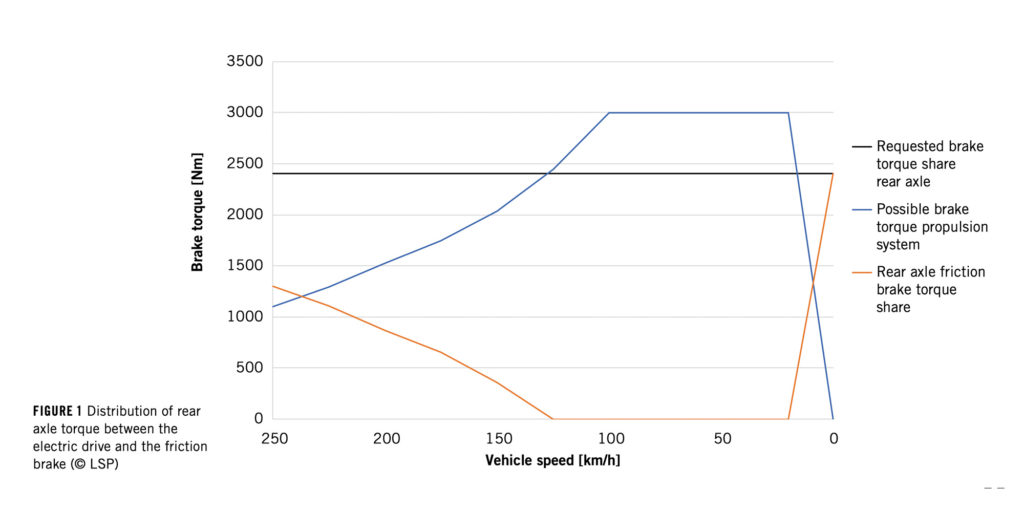
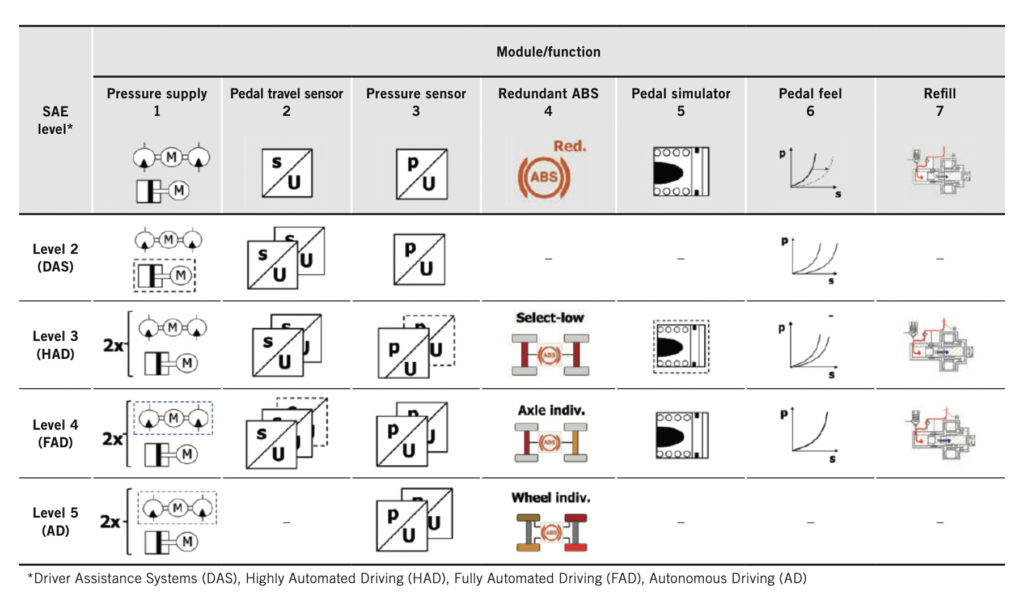
The development processes of nuclear power plants and of aerospace are applied to the development of brake systems for automation levels HAD to AD, since the highest safety levels are needed for AD. The usually relevant fallback solutions “fail silent” and “fail safe” will be replaced by “fail operational” with the start of the HAD phase. This means that in the event of a failure or of a partial failure, the basic functionality must be preserved.
While hardware and software development is subject to clear standards in the analysis method of failures, these do not yet exist in the area of mechanics and hydraulics. The basic methodology and approach is known. The aim is to create a functional and safety concept with a definition of diagnosis and distinguish between active and passive failures. In the case of hardware and software, ISO 26262 is applied. This involves the use of proven tools and sufficient experience with failure rates in order to prepare the analyses. In mechanics and hydraulics, the emphasis is on the application of FMEA and FTA. Failure analysis considers failures and their effects using failure rates of components and systems, expressed in ppm per vehicle life time. A problem is a new or modified design, if failure rates are not yet available. In order to meet the high safety standards, diagnosable redundancies for important functions are required. TABLE 1 shows possible failures, problems with their effects and diagnosis possibilities of some specific critical components of brake systems such as piston seals, solenoid valves and ball screws. With open brake systems, the wheel circuit is hydraulically connected to the reservoir by opening the outlet valve during ABS control. Undetected leaks in valves and seals (dormant failures) require special consideration with open brake systems. If a solenoid valve with a dormant failure, for example, connects both brake circuits, then a brake circuit failure leads to a PS failure and, as a worst-case scenario, the entire brake system may fail. For this reason, closed brake systems are preferable. In addition to these hydraulic and mechanical failures, failures in the vehicle electrical system are of great importance, as will be discussed in the following.